ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING

ERP systems currently exist in many different forms and offer many different features. Various businesses, large and small, have implemented ERP systems. Implementing an ERP system can be a daunting and expensive undertaking. A business seeking to purchase and implement an ERP system should perform extensive due diligence on the available systems and suppliers.
Major Reason for adapting ERP:
- Integrate financial information
- Integrate customer order information
- Standardize and speed up operations processes
- Reduce inventory
- Standardize Human Resource Information
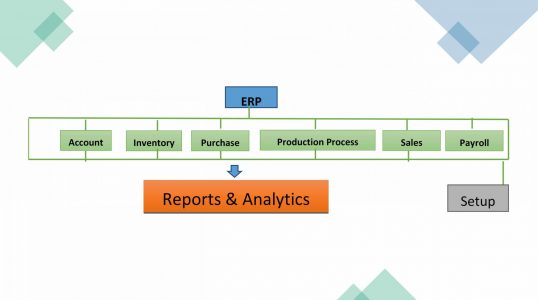
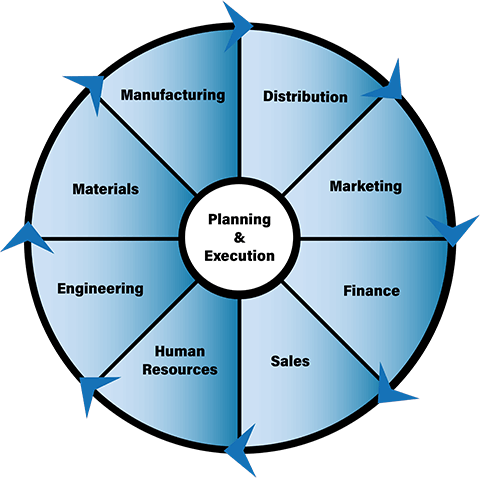
How do ERP system work?
Finance: Financial modules for bookkeeping and making assure the bills are paid on time. Examples are like:
- ⦁ General leader
- ⦁ Accounts Receivable
- ⦁ Accounts payroll
HR: Software for handling personnel-related tasks for corporate managers and individual employees. Examples are like
- ⦁ HR administration
- ⦁ Payroll
- ⦁ Self-service HR
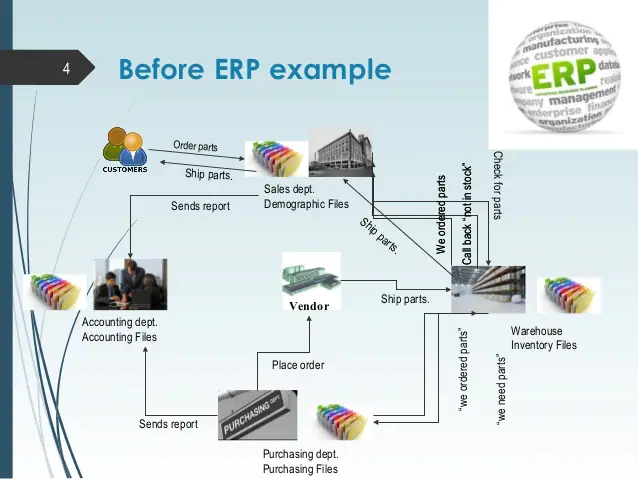
An ERP Example of Before & After
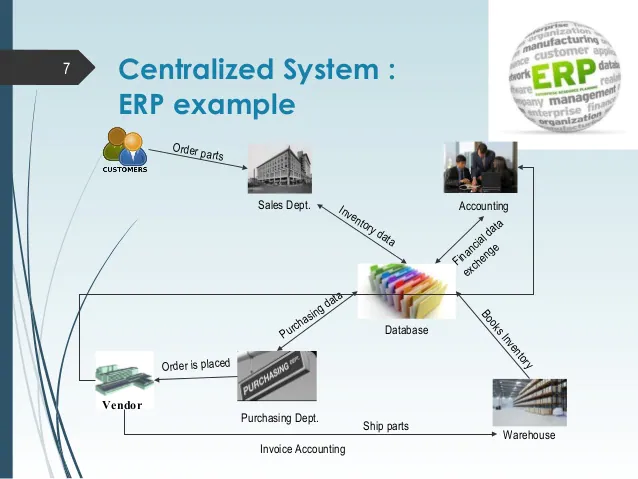
- ⦁ improve efficiency
- ⦁ information integration for better decision making
- ⦁ Faster response time to customer queries
- ⦁ Expensive
- ⦁ Time-consuming
- ⦁ Greater risk for organization
- ⦁ Acceptance with the company
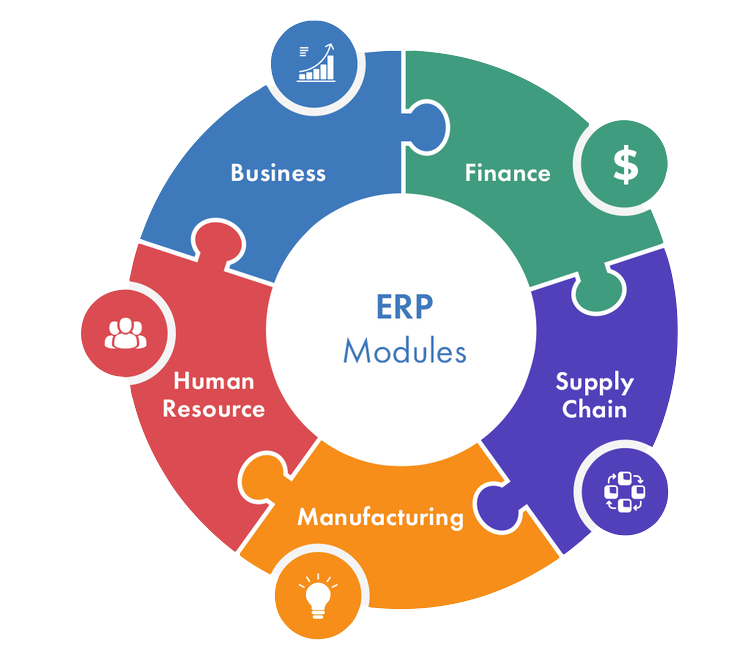
- ⦁ Finance
- ⦁ Material
- ⦁ Sales
- ⦁ Marketing
- ⦁ Personnel
ERP Finance Module: An ERP finance module gathers function data and turns them into reports including quarterly financial statements, ledgers, profit tracking, and balance sheets.
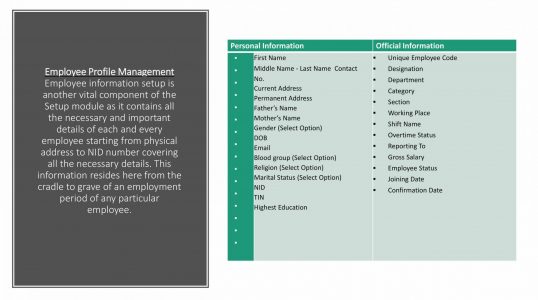
ERP HR: Module routinely maintain a complete employee database including contact information, Salary details attendance, Promotion of all employees.
- ⦁ Produce paycheck reports.
- ⦁ Maintain personnel record.
- ⦁ Training
- ⦁ Time and attendance benefits
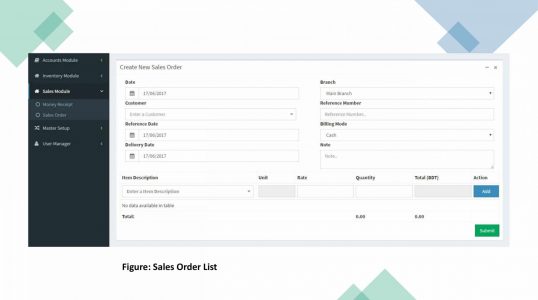
ERP Purchasing Module: Purchasing module is tightly integrated with inventory control and production planning modules.
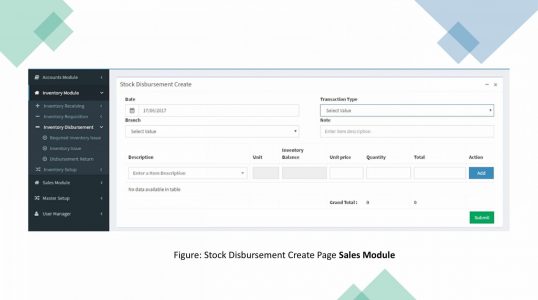
ERP Inventory Module: Inventory module facilities processes of maintaining the appropriate level of stock in a warehouse.
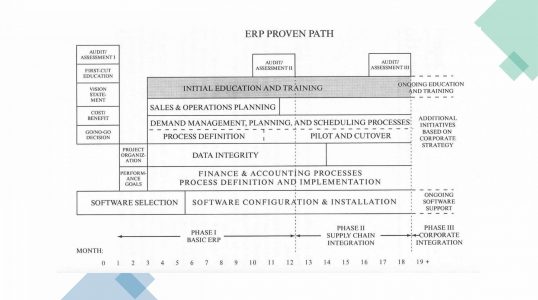
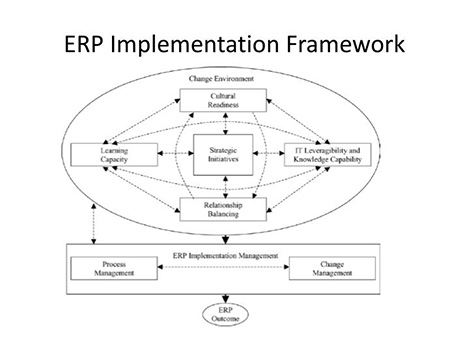
Implementation of ERP
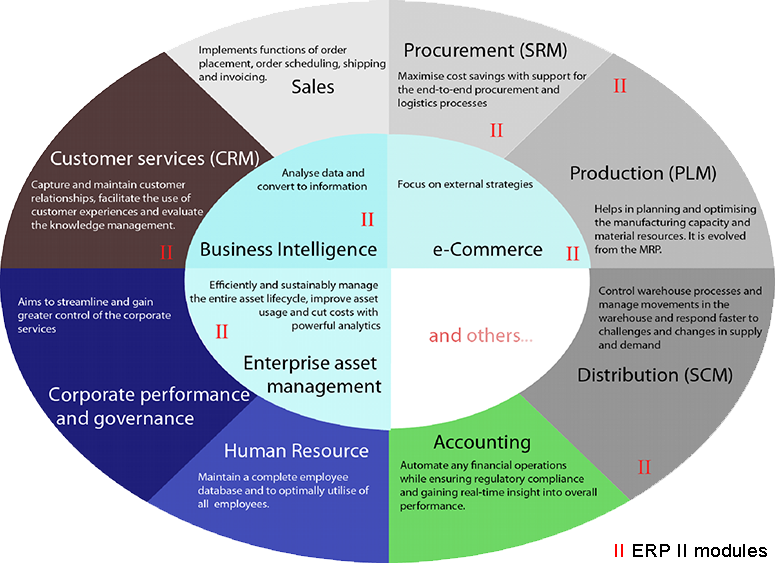
ERP Implementation Approaches:
- ⦁ The big bang - install a single ERP system across the entire organization.
- ⦁ Franchising - Independent ERP systems are installed in different units linked by common processes, such as bookkeeping.
- ⦁ Slam dunk – Install one or several ERP modules for phased implementation of key business processes.
Major Phases of ERP Implementation:
- ⦁ Initiation – Develop business case, project scope and implementation strategy.
- ⦁ Planning – Establish implementation team, determine goals and objectives, establish metrics
- ⦁ Analysis and process design – Analyze and improve existing processes, map new processes to be adopted by system.
- ⦁ Realization – Install a base system, customization and test the system.
- ⦁ Transition – Replace the formal system with the new system, data conversion.
- ⦁ Operation – Monitor and improve system performance, provide continued training and technical supports.
ERP Implementation Approaches:
- ⦁ Education and training
- ⦁ Availability of internal technical knowledge and resources
- ⦁ Implementation timelines
- ⦁ Flexibility of software system upgrades
- ⦁ Changes in employee responsibilities
- ⦁ Costs – Implementation (hardware, software, training, consulting) and maintenance
- ⦁ Inconsistency with existing business processes
- ⦁ Limitations of ERP technical capabilities
- ⦁ Implementation strategy and execution
- ⦁ Resistance to change
Advantages of ERP:
- ⦁ Quicker completion of processes
- ⦁ Single software
- ⦁ Database
- ⦁ Easier to track various tasks
- ⦁ Manage globally Data
Disadvantages of ERP:
- ⦁ Cost
- ⦁ Time Consuming
- ⦁ Training to employees